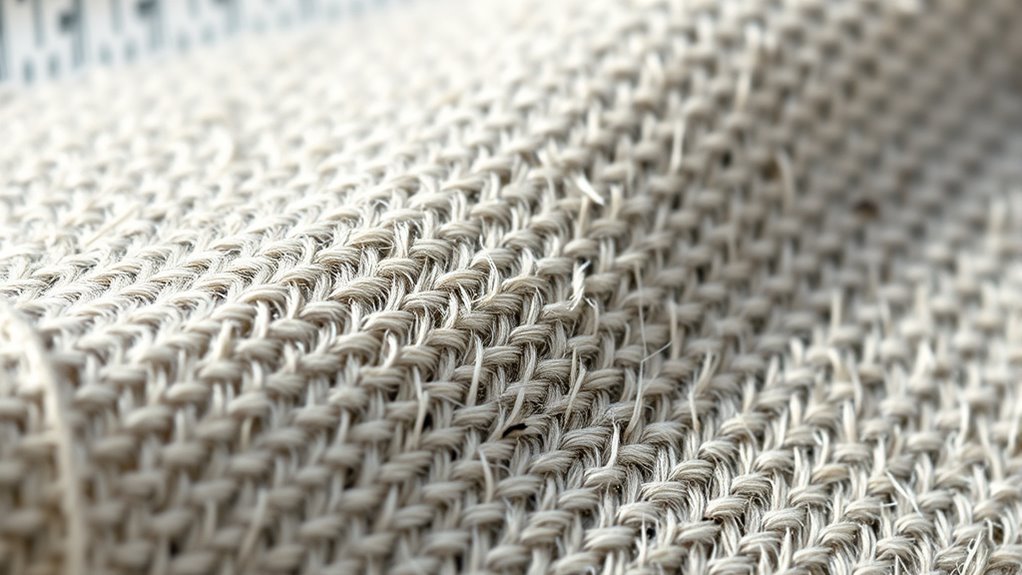
GSM in fabric weight stands for Grams per Square Meter, which measures how heavy or thick a fabric is by calculating its mass over a specific area. Think of it as how much material you’ve got in a square meter of cloth. The higher the GSM, the thicker and more durable the fabric becomes. If you want to explore the simple math behind GSM and how it impacts fabric choice, there’s more to discover just ahead.
Key Takeaways
- GSM (Grams per Square Meter) measures fabric weight by weighing a specific fabric area and calculating grams per square meter.
- It indicates fabric density, affecting durability, thickness, and suitability for different applications.
- To determine GSM, cut a sample, weigh it in grams, and divide by its square meter area.
- Higher GSM fabrics are heavier, denser, and generally more durable, while lower GSM fabrics are lighter and more breathable.
- GSM provides a simple way to compare fabric weights regardless of fabric size or type.

Have you ever wondered how your mobile phone connects so seamlessly to your network? Behind that smooth connection lies a complex web of technology, including fiber optic cables that form the backbone of modern communication infrastructure. Understanding fiber types and manufacturing processes can give you a clearer picture of how data travels at lightning speed across vast distances. Fiber types mainly include single-mode and multi-mode fibers, each designed for specific applications. Single-mode fibers have a tiny core, allowing light to travel straight through with minimal loss, making them ideal for long-distance communication. Multi-mode fibers, with their larger cores, are better suited for shorter distances and higher data rates within data centers or local networks. Knowing which fiber type is used helps you appreciate the precision involved in building reliable, high-capacity networks. The manufacturing processes of these fibers are intricate and demand meticulous quality control. They start with high-purity silica, which is melted and drawn into thin fibers through controlled heating and pulling. During this process, the fibers are coated with protective layers to prevent damage and minimize signal loss. These coatings are essential because they help maintain the fiber’s integrity during installation and operation, ensuring consistent performance over time. Fiber manufacturing also involves rigorous testing, including assessments of strength, flexibility, and signal attenuation, to guarantee that each fiber meets industry standards. This attention to detail is what allows fiber optic networks to handle enormous amounts of data with minimal interference or degradation. When data signals are sent through these fibers, they are converted into light pulses that travel at incredible speeds. In the context of GSM technology, this means voice and data transmissions are transmitted efficiently, supporting seamless mobile connectivity worldwide. The fiber types and manufacturing methods work together to create a robust infrastructure, capable of supporting the ever-growing demand for faster, more reliable communication. So, the next time you make a call or browse the internet on your mobile device, remember that a combination of carefully selected fiber types and precise manufacturing processes makes it all possible. These elements form the silent backbone of GSM networks, enabling your device to connect effortlessly and transmit data swiftly across oceans and continents. Without this sophisticated technology, the simple act of staying connected would be far more complicated and slower. It’s a marvel of engineering that ensures your communication remains uninterrupted, efficient, and secure, all thanks to the intricate world of fiber optics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is GSM Different From Thread Count?
GSM measures fabric weight based on fiber density per square meter, reflecting fabric thickness and overall heaviness. Thread count, however, counts the number of threads woven in one square inch, focusing on fabric’s fineness and texture. While GSM indicates how heavy or thick the fabric is, thread count relates to its softness and durability. Both metrics help you understand fabric quality, but they measure different aspects of the material.
Can GSM Be Used for Non-Fabric Materials?
You might wonder if gsm can be used for non fabric materials. The answer is yes, gsm applications extend beyond fabrics. It measures the weight per square meter for various materials like paper, insulation, or even plastics. This standard helps you compare thickness and density across different non fabric materials, making gsm a versatile measurement tool. So, whether you’re working with paper or other materials, gsm provides useful insight into their weight and quality.
What Factors Influence Fabric GSM Besides Weight?
When you consider what influences fabric gsm beyond just weight, fiber density plays a key role—denser fibers mean higher gsm. Manufacturing processes also impact gsm, as techniques like weaving, knitting, or finishing can alter the fabric’s thickness and weight. So, if you’re evaluating fabric quality, look beyond gsm and consider how fiber density and production methods shape the fabric’s overall feel, durability, and performance.
How Does GSM Impact Fabric Durability?
Think of GSM as the armor that shields your fabric’s longevity. Higher GSM fabrics are like sturdy castles, offering better wear resistance and lasting longer through daily use. When GSM is low, the fabric becomes more prone to wear and tear, reducing its durability. So, by understanding GSM, you can choose fabrics that stand the test of time, ensuring better wear resistance and extended fabric longevity.
Is GSM Measurement Standardized Across Industries?
You might wonder if GSM measurement is standardized across industries. While GSM provides a useful way to compare fabric weights, standardization challenges exist due to industry variations and differing testing methods. Some sectors may follow specific standards, but overall, GSM isn’t universally consistent. This means you should consider industry-specific guidelines when evaluating fabric weight, ensuring accurate comparisons and selections for your projects.
Conclusion
Now that you understand GSM, it’s like having a fabric’s heartbeat—telling you how heavy or light it truly is. With this simple math, you can easily compare fabrics and choose what’s best for your needs. Think of GSM as the weight of a book’s pages; the higher the number, the thicker and more substantial it feels. Armed with this knowledge, you’re ready to make smarter, more informed fabric choices every time.